
Bharat NCAP safety rating protocol will include frontal impact, side impact and side pole impact tests awarding star rating for adult occupants (AOP) and child occupants (COP)
Bharat New Car Assessment Program (Bharat NCAP) has been rolled out by Ministry of Road Transport and Highways under Union Minister Nitin Gadkari. Under this program, automakers will be able to offer their cars for testing as per Automotive Industry Standard (AIS) 197. Testing done under BNCAP will change the automotive scenario in India. While buyers will be assured of vehicle safety, automakers will be able to compete on a global platform. It will also help introduce safer driving practices, reduce the onus of healthcare and garner incentives from the insurance sector.
Benefits of testing cars under Bharat NCAP
Set to come into effect from 1st October 2023, this will make India the 5th country to have its very own crash testing rating system. Following its successful launch, as many as 30 cars have already been offered for crash testing under Bharat NCAP. It will involve a cost of around Rs. 60 lakh when done in India which would escalate to Rs 2.5 crores if a similar test were to be conducted overseas.
Even as testing cars under Bharat NCAP is voluntary, buyers seeking more safety as they move from being cost-centric to safety-centric will drive automakers to get their vehicle tested under these new stringent norms. It will lead to comparative safety aspects of various products giving buyers the choice to select their vehicle on the basis of safety ratings. It will also go a long way in minimizing the risk of road accidents and fatalities while for automakers, testing would ensure a higher market share while being able to compete on a global platform. It will also lead to development and use of cutting-edge components and encourage innovation.
Qualification of Cars under the Bharat NCAP Crash Test Regulations
Bharat NCAP is subject to rules and regulations. For starters, eligibility will include all vehicles falling under the M1 category, approved for carrying upto 8 passengers +1 driver. The vehicle should have a gross weight lower than 3.5 tonnes and can be either manufactured locally or imported. All combustion engine, CNG and electric vehicles will come under the scope of Bharat NCAP.

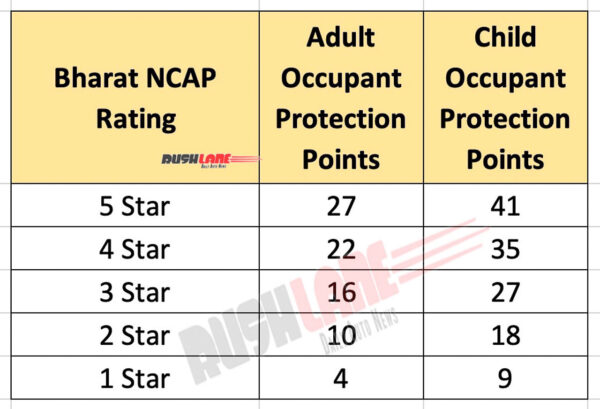
The cars will be assessed on basis of frontal impact, side impact and side pole impact. It will cover three areas of Adult Occupant Protection (AOP), Child Occupant Protection (COP) and Fitment of Safety Assist Technologies and star rating of 1-5 will be awarded for cars tested with 5 Stars being the highest rating. Separate stars will be allocated for AOP and COP.
Frontal Impact Tests are performed at 64 km/h or 40 mph. The car is made to crash into a deformable barrier with 40 percent of front width on the driver’s side, the same as that seen on Global NCAP tests. Crash test dummies are used to assess protection of adults in the front seat. The cars will also need to comply with pedestrian protection norms. In the event of a vehicle attaining safety rating of 3 stars or higher, it will be subject to an additional pole-side impact test
Side-crash and pole-side impact tests will be done at 50 km/h and 29 km/h, respectively. Each category is allotted maximum and minimum points, to determine its star rating. For example, a vehicle must be equipped with front seat belt reminders and electronic stability control to achieve a three-star rating. Bharat NCAP star ratings are upto a maximum of 32 points for AOP and 49 points for COP.
Procedure for Crash Tests under Bharat NCAP
– The automaker will have to nominate a vehicle for crash testing.
– Authorities from Bharat NCAP will visit the company stockyard and select a base variant of the vehicle at random.
– The vehicle will then be dispatched to the Bharat NCAP facility wherein witnesses from the automaker will be present along with BNCAP officials during the tests.
– Test results will be compiled and revealed to the automaker following which they will be published and a certificate issued by Central Institute of Road Transport.
In conclusion, while Bharat NCAP takes into account car safety, Gadkari called on agencies such as Automotive Research Association of India and National Automotive Test Tracks to develop in-house crash testing facilities. He also raised the awareness of road engineering which is also an area to be tackled so as to reduce accidents and fatalities across India’s roads which currently witnesses 47 accidents and 18 deaths per hour with 70 percent of road accident fatalities occurring within the age groups of 18-34 age group.

