
With its huge untapped potential, EV segment in India has been attracting startups and tech companies in droves
Chinese smartphone manufacturers have been following an aggressive strategy ever since the telecom revolution started to take shape in India. With their affordable pricing and advanced features, the likes of Xiaomi, Realme, Oppo, Vivo, OnePlus, etc. have been able to establish a strong presence in the country.
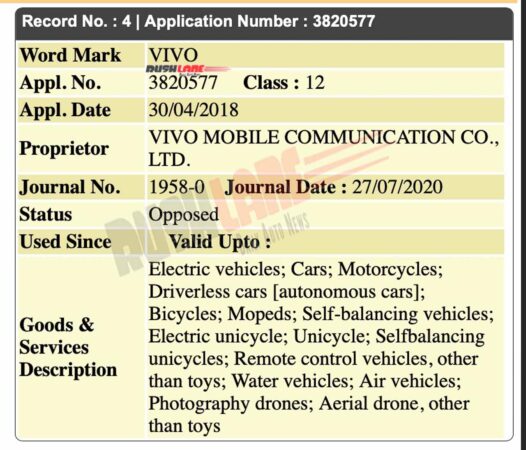
As the next big thing in India will be EVs, these companies are planning to target this space as well. Most of these smartphone manufacturers including Vivo have filed their respective trademarks in automotive category. The status of Vivo’s trademark application currently shows up as ‘opposed’.
Vivo Electric Scooter, Motorcycles, EV details
It is not yet certain what type of EVs Vivo is planning to launch in India. A specific timeline for launch of these EVs is also not available at this point of time. As per the trademark application filed under Class 12, the category lists a wide range of goods and services.
It includes electric vehicles, cars, motorcycles, driverless cars (autonomous cars), bicycles, mopeds, self-balancing vehicles, electric unicycle, unicycle, self-balancing unicycles, remote control vehicles, water vehicles, air vehicles, aerial drone and photography drone.
Considering that electric two-wheeler segment is among the ones with highest potential, Vivo could start its EV journey with an electric scooter and/or an electric motorcycle. It’s too early to comment on the design of Vivo electric two-wheeler, but it will be safe to assume that it will pack in a range of advanced features.
Things likes keyless entry, voice commands and a comprehensive range of connectivity features could be on offer. Vivo is among the premium smartphone brands in the country and it will like to maintain a similar status in EV space as well.
Easy access to battery and parts
Chinese handset manufacturers like Vivo will have several advantages that will allow them to crack the Indian EV segment. As of now, China is a hub for battery technology and manufacturing. Most of the current electric two-wheeler brands in India rely on imported battery packs and related components. Smartphone makers like Vivo will have easy access to supplier network in China and they can strike better deals at local level.
Electronics is another area where smartphone manufacturers are destined to take the lead. EVs utilize a fair amount of electronics, a need that companies like Vivo can easily fulfil. Another advantage is that brands like Vivo, Xiaomi, Oppo, OnePlus, and Realme are already popular in India. Consumers will feel more confident when buying EVs launched by these companies.
Chinese brands are known for playing the numbers game. This strategy is likely to be deployed in EV space as well. Homegrown manufacturers like Ola Electric, Bajaj, TVS, Ather, Simple Energy, Revolt, etc. will be following these developments closely. A tough battle is expected ahead.

